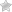Potato soup is a hearty meal in and of itself, rich and creamy with tender potatoes. Served in a bread bowl, this recipe takes it to a whole new level. Bread bowls are extremely popular, and for good reason. Bread is one of the most beloved foods in the world, so of course a bowl made out of it is going to be a hit.
Bread bowls became popularized through Panera Bread for many people. Although Panera Bread has alternated between offering and not offering bread bowls over the years, the consensus is still that it's one of their best options. Being able to create that experience at home is great.
This recipe isn't difficult. You'll only need five ingredients to make this, which is fantastic. Many soup recipes, including potato soup, have way too many ingredients. Nobody wants to stare at a page-long list of things they need to add to their grocery list.
On top of that, each step for this recipe is simple and straightforward. No unnecessary guesswork, no hassle, and little room for error. As long as you follow each step exactly as written, you'll have an amazing dinner to serve your family in no time at all.
Print
Bread Bowl Potato Soup Recipe
Ingredients
- 1 14–ounce can reduced-sodium chicken broth
- 1 20–ounce package refrigerated diced potatoes with onions
- 1 cup whole milk
- 1 8 ounce package shredded cheddar cheese
- 4 purchased bread bowls (optional)
Instructions
- In a large saucepan bring chicken broth to a boil.
- Add potatoes; return to boiling. Reduce heat.
Simmer, covered, for 10 minutes or until potatoes are very tender.
Remove from heat.
Cool slightly.
Place half of the potato mixture in a food processor bowl or blender container. Leave half in the saucepan.
Cover and process or blend until almost smooth, leaving some pieces of potato.
Remove and add to the remaining potato mixture in the saucepan.
Stir in milk, heat through. Season with salt and ground black pepper.
Divide soup evenly between four bread bowls.
Sprinkle cheddar cheese on top of each bowl while soup is still hot. Serve immediately.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©MomsWhoThink / MomsWhoThink.